Determining a camera’s pose from images – known as visual localisation- is fundamental to applications from autonomous driving and robotics to augmented reality, yet existing datasets face two key issues. They either lack the scale needed for large-scale scenes, limiting progress towards truly scalable methods. Second, when they do cover large scenes, they often provide imprecise ground truth poses for the query image data. egenioussBench overcomes these limitations by pairing a high-resolution aerial 3D mesh and a CityGML LoD2 model as geospatial referee data and a map-independent ground-level smartphone imagery with centimetre-accurate poses obtained via PPK and GCP/CP-aided adjustment as query data.
The benchmark offers:
- A high-resolution aerial 3D Mesh and a CityGML LoD2 model as geospatial reference data
- A test split of 42 non-co-visible query images with withheld ground truth
- A validation split of 412 sequential query images with released poses
- A public leaderboard, evaluated with multi-threshold binning metrics and comprehensive global statistics
More information and the full dataset and the leaderboard are available here. You can find the benchmark publication here.
egenioussBench is provided through the EU-Horizon project egeniouss, which received funding under the call HORIZON-EUSPA-2021-Space with the project number 101082128.
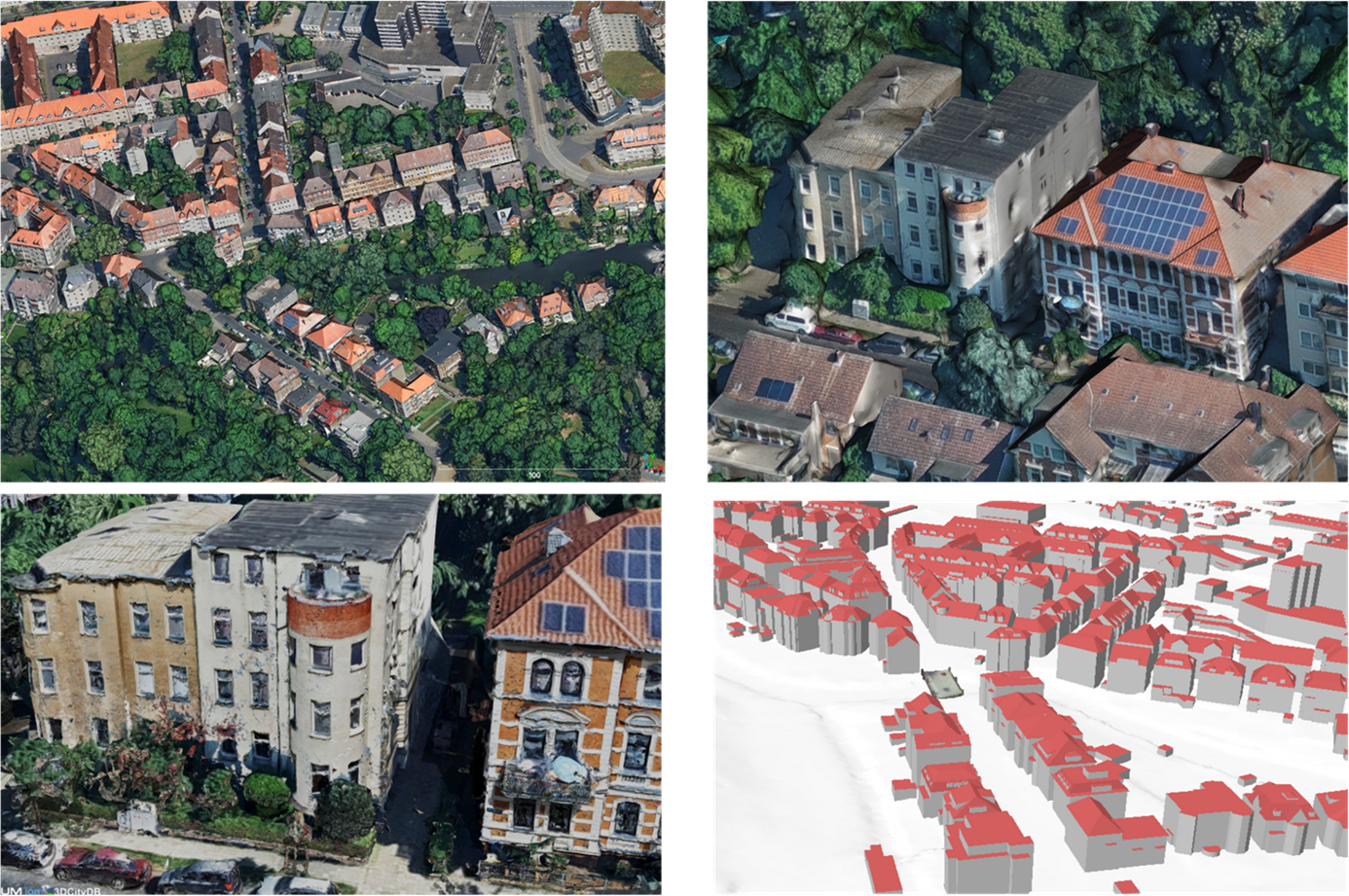

Overview of ground truth data

Example query images
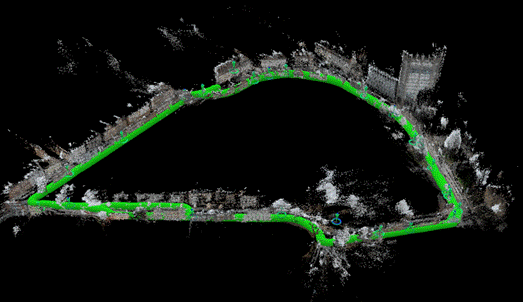
Area in Braunschweig city, reconstructed from all query images